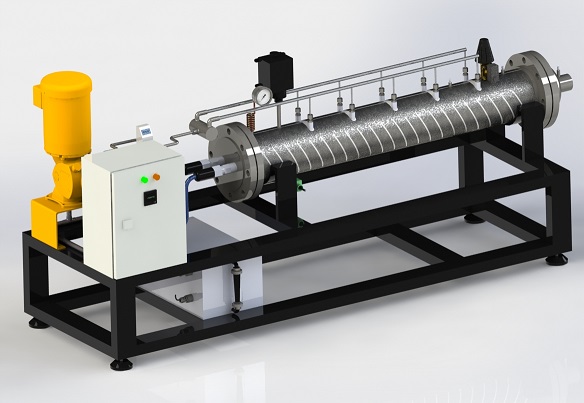
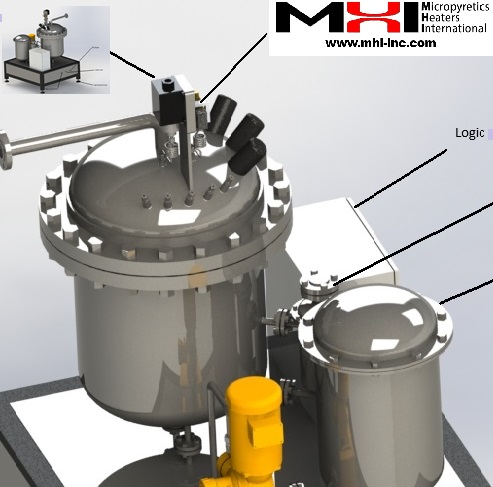
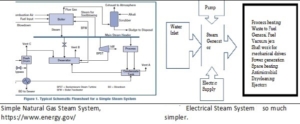
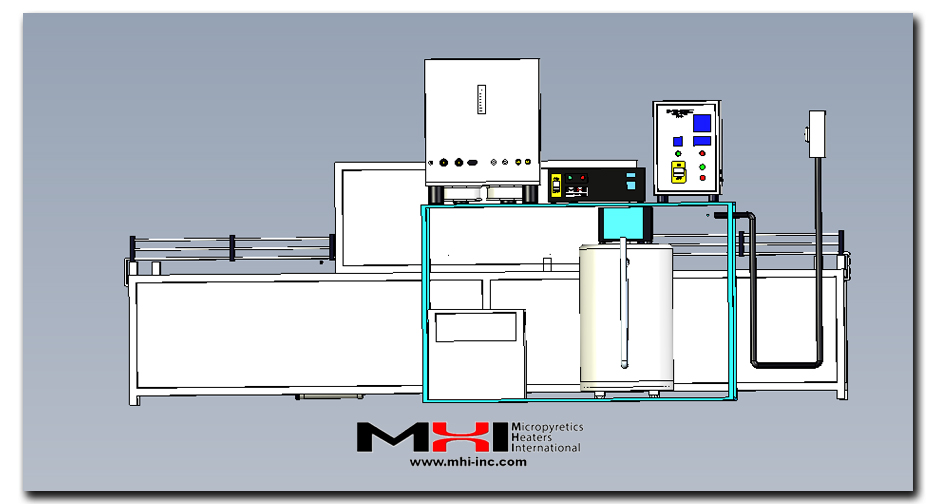
Steam Generation Technology with Major Energy and Water Savings.
Available from low kW to MW for both low and high steam flow requirements. It’s easy to operate: just set the flow and temperature, then press start. Quick start-up and shut-down help save energy overall.
Reduce the carbon footprint to zero for steam generation through deep decarbonization. Eliminate GHGs. Monitor load on the HMI display. Set the maximum power and control energy costs. The versatile OAB significantly simplifies the optimization of any steam generation process.
What are the advantages of an electric steam generator over a conventional boiler? A highly compact steam generator, such as the OAB or Mightysteam, enables control over power, steam flow rate, and exit steam temperature. Steam generators enable process optimization with precise temperature control, enhanced energy efficiency, pressure variability, steam-flow rate control, and desired pulsing. They can quickly turn on and off, requiring minimal to no idling and delivering unrivaled durability. It’s an excellent solution for high-usage operations, designed to withstand thermal expansion and eliminate steam leak points. ![]()
Click for Typical Electric Steam Generator Product Models

Use a modern steam generator when the application requires the following:
- The steam quality required is higher than that of saturated steam for improved productivity, chemical cleanliness, power delivery, and antibacterial efficacy.
- When energy efficiency is critical, compare the energy used to heat water from room temperature to the temperature at which it is used.
- For comfort heating with high energy efficiency*.
- For processes that need variable temperature and variable flow rate, e.g., drying, chemical reactions, fuel production with reaction temperatures as high as 1200 °C for steam. Several new processes utilize steam at temperatures exceeding 500 °C. Productivity and process efficiency often increase with temperature.
- For clean steam use in pharma or food sectors. A clean steam application requires dry steam, meaning there is no water (with dissolved impurities) in the steam.
- Modern installations use touch-screen controls to activate and regulate steam (instead of struggling with several rusted, stuck valves). Such features improve efficiency and productivity.
- Local steam codes met with UL, ASME, and CRN regulations.
- Directly control steam processes and humidity. The instant steam generators directly sense signals to regulate the steam rate and the set temperature automatically.
- Introduction to Steam and Humidity, Steam Generators and their Applications
When burned, one kilogram of natural gas releases 2.75 kilograms of carbon dioxide (CO2), and one cubic meter of natural gas releases 1.9 kilograms of CO2, or 380 kilograms of CO2eq. The social cost of CO2 emissions is very high.
Please specify output temperature (choose saturated to 1200C (2200F) or more)
GOAB-6 Variable flow (2-6 Kg/hr. Steam)
OAB-4 Fixed flow 4 Kg/hr. Steam
OAB-Var 25 Kg/hr 750C (15-25 Kg/hr.) – syngas production starter model (25 Bar).
OAB-50-Var- Models (20-60 Kg/hr. Steam)
OAB-100-Var-Models (70-120 Kg/hr. steam)
OAB-180-Var Models (120-220 Kg/hr. Steam)
OAB-360-Var Models (240-440 Kg/hr. Steam)
OAB-750-Var-Models (360-660 Kg/hr. Steam)
OAB-1200-Var-Models (1.2 Tons/hr. Steam)
OAB-2700-Var-Models (3 Tons/hr. Steam)
Video: OAB Unit 360 view (download)
Technical Specifications of Steam Generators
| Model | Image | Temp. Range | Pressure Rating | Efficiency (nominal best to use only as an approximate guideline) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MightySteamOAB (variable) Premium model with variable flow rate and temperature features. Heavy Industrial. |  OAB Electric Steam Generators. Decarbonized. | Up to 1200°C Models from 5 kg.hr to tons/h, kW to MWModern electronic flow rate valves and HMI settings. | Atmospheric- 40 bar | High 95%+ | Sterilization, chemical processing, food industry, CPG packaging. Pharmaceutical, textiles, HVAC, Testbeds. More Information |
| HGA-Sor OAB fixed Models for innovation prototyping. |  HGA-S-01 HGA-S-01 OAB-12-750 | 300-1200°C 1 kg/h.with steam side valveorOAB, fixed flow 4 or 12 kg/h (fixed) with steam side valve. 750°C temperature | Atmospheric | 95%+ | Sterilization, chemical processing, food industry, CPG packaging. Pharmaceutical, textiles, HVAC, Testbeds. More Information |
| HGA-M |  | 300-800°C 1 kg/hr. or 4 kg/h. | Atmospheric | 95%+ | Medical sterilization, laboratory applications, and mobile applications More Information |
*Our experience indicates that an electric steam generator can be almost 50% more efficient in energy use than a fossil fuel steam generator and 25% more efficient than a conventional electric pressure boiler. (Approximate comparison only – individual situations can vary – please get in touch with MHI for details and assumptions used – Note 1 BHP~9.6KW.
Where a fuel-fired steam boiler or any other fossil fuel-based heater operates appropriately with a predictable maintenance schedule, the proper inspection takes weeks with highly experienced technicians and specialized tools. This means production downtime, which is the most significant cost to industrial facilities. In unexpected failures, plant shutdown can take longer, contributing to more opportunity costs. Electric systems are far less complex.
Depending on the assumptions for CO2 emission costs, an electric steam generator will likely cost less and operate with lower costs than conventional boilers.
Click for Electric Steam Generator Product Model Numbers
Reduce water wastage with the OAB MightySteam smart steam generator. It is easy to install, simple to use, and cost-effective. Optimize—use only the amount of water required—save considerable energy.
Contact MHI. Choose from a Single Phase (1 -20 Kg/h (kW systems) to three-phase (25-9000Kg/h, MW power systems). Please specify the temperature, flow rate range, and required back pressure. Temperature choices from 150°C, 200°C, 300°C, 550°C or 750/800°C and 1300°C. Steam Generator Models.
Steam Generator Models.
- OAB® Models. 60 kg/hr -6000 Kg/hr. steam
- GOAB Models 2kg/hr – 40 kg/hr.
- Laboratory 1 kg/hr Models. Steam HGA, Steam-Air Mix HGA-M.
Is it time to upgrade to a more reliable, easy-to-use, instant electric steam generation system with built-in modern energy-saving features? Upgrade to a generator that offers independent control over the steam flow rate, temperature, and backpressure. MHI high-temperature steam allows everyone easy access to clean steam that does not contain boiler residue, chemical or bacterial contaminants, or other undesirable solid substances.
Unlike conventional boilers, patented MHI steam generators make instant,t high-quality, superheated, dry steam above the inversion temperature.
Flexibility in the steam characteristics leads to enhanced energy efficiencies, accurate process control, and water savings. MHI steam generators with touch-screen inputs offer features like electrical on-off (on-demand steam) and management of steam operations with signals from external sensors (humidity meters, concentrators, valves).
Industrial Models.
- GOAB™ with variable temperature and variable steam rate adjustment. Several models.
Today, the need for high-quality, clean electric steam also encompasses zero emissions, high energy efficiency, and minimum spatial footprint configuration requirements. The MightySteam® and OAB® steam generators produce non-condensing steam above the inversion temperature. Because there are no liquid droplets, the steam is of high quality. This improves steam performance for pharmaceutical use, clean comfort, and utility.
When converting from fossil fuel energy to electric energy, steam generation, the following aspects may be helpful to consider:
- The OAB® steam generators operate at 98% or better efficiency at typical utility-steam temperatures. Because the efficiencies are higher for the same energy use – please consider if the requirement for power used can be reduced when converting to electric steam generators.
- Electric boilers are small and emit no gas. Therefore, several smaller electric boilers can be used instead of one large boiler.
- Electric steam generators’ on-off capability, variable temperature, and variable flow-rate features can help save energy.
- High-temperature steam, typically from electric steam generators, can accelerate several chemical processes for higher productivity gains. The steam generator does not need to operate at high pressures to produce high-temperature steam.
With this modern energy and time-saving steam generator, there is no need for superheaters or boilers to 800°C+ for high-quality clean steam. There are no combustible fuel oils or gases, no intense magnetic field, and no heating of flow pipes by induction. The temperature measured is that of the steam, not of the line.
Self-cleaning systems – save in downtime and labor hours.
Click here to send us your requirements for a variable steam rate, variable temperature, variable backpressure, and instant on-off steam generation. Temperature choices from 150°C, 200°C, 300°C, 550°C or 750/800°C and 1300°C.
R&D and Process Development Models.
- 1 Kg/hr with temperatures from low to 1300C.
- 4Kg/hr and 12Kg/hr Fixed Steam Flow Models
- 6 Kg/hr and 12 kg/hr variable flow steam and temperature up to 800C and beyond.
- Click for mixed Air-Steam models HGA-M
- Click for Steam Chambers for R&D
Link to a Brief History of Steam Production Methods
Introduction to various types of steam and humidity
Why is the MHI Electric Steam Generator Efficient? The HGA, GHGA, and OAB® steam generators have been a product of intense R&D and customer acceptance over the past decades. These modern steam generators use surface enhancement nanotechnologies, optimized  high-impact heating materials, unique designs, and efficient control electronics. MHI Inc. holds several current patents in materials and heater designs. The graph below shows one example of MHI’s significantly improved materials in its build.
high-impact heating materials, unique designs, and efficient control electronics. MHI Inc. holds several current patents in materials and heater designs. The graph below shows one example of MHI’s significantly improved materials in its build.
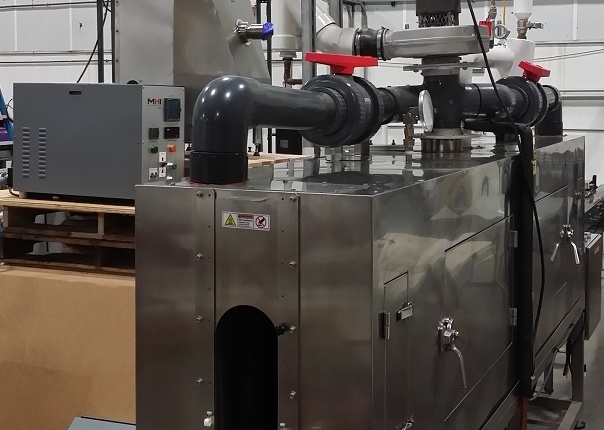
Deep Decarbonize and High Efficiency with MHI Steam Generators: Unlike traditional boilers, which lose significant efficiency with pressure, Steam generators typically operate with high efficiency and allow operation at the minimum back process pressure required regardless of the temperature of the steam output. The efficiency is higher than 95%, even close to 98%, with rapid heat up within minutes for dry steam, touch screen safety features, zero CO2, and zero NOx. The generators offer variable steam flow and variable back pressure for constant temperature. The units are built to the highest level of user-preferred ASME codes. Modern ethernet protocols and electrical code compliance are offered. Contact MHI.
MHI Electric Steam Generators are clean: Older steam boilers are fuel-fired (fossil-fired) and may use biofuels, coal, natural gas, and byproduct materials. The composition of exhaust gases from a boiler depends on the type of fuel used and may need cleaning treatment if they contain pollutants such as CO2, CO, SO2, Soot, Ash, NOx, and particles. MHI steam generators do not produce or emit these. Traditional boilers require boiler rooms and a certified workforce. Compare energy efficiencies of different methods of making steam.
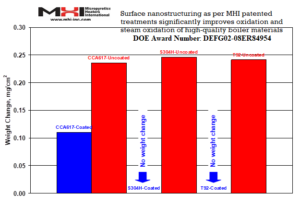
The patented MHI nano-material treatment of boiler steel materials shows a significant decrease in humid air oxidation and steam oxidation rate at high temperatures.
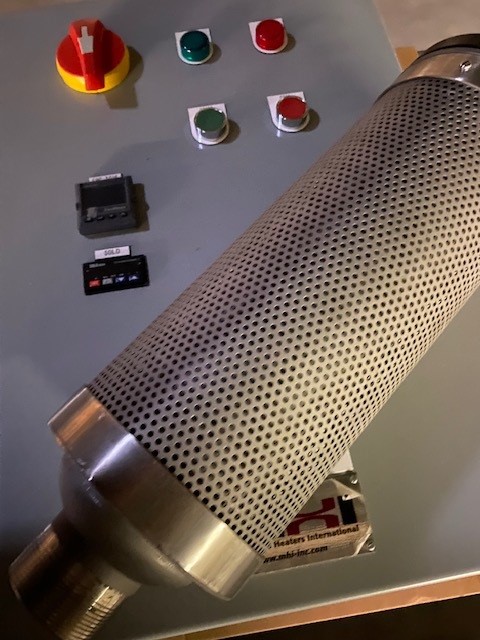
The MHI Steam Generators work hard for you. Depending on the model, they monitor the incoming electric phase variations, steam temperature, and steam flow rate, display any developing faults, and accept a host of user input controls. They even monitor the quality of water.

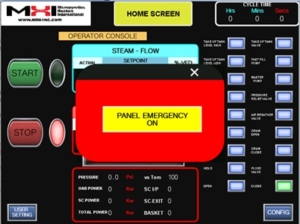
OAB steam generator software control
Steam Superheaters, Low-Pressure Steam Generators, Industrial Electric Steam Generators for Utility and Process use, High-Pressure Steam Generators, Steam Generators, Electric Steam Generator, Superheated Steam Generator, Clean Steam Generator, Steam Generators, Inline steam, Shrink Fitting for Packaging.
Modern Steam. MightySteam® products reduce the price of high-quality steam. Enjoy high conversion efficiencies, and save water.
Modern PLC, SCR, HMI (touch screen) operation. Remote communications and control.
MightySteam® Products (Industrial and R&D Use)
MigthySteam® Controlled Humidity Products (Commercial Use)
Use less energy for the same outcome.
Energy savings with steam for deep decarbonization.
Energy Content and Combustion Efficiency of Fuels that are Used for Steam Generation.(Source) | Comparison of CO2 Emissions One million BTU of fossil-fuel combustion energy (i.e., ~1055055 KJ) can make ~380 Kg of 100°C steam. The mass of carbon dioxide in lbs., produced with one million BTU, is given below. | |||||
| Fuel Type /Energy Unit | Typical Temperature of Steam | Conversion Efficiency, %. Common Range. | Idling Required | Requirement of Super-structure and Water Feed Treatment. | ||
| *Natural Gas/ MMBtu | 100-132°C | 80-86 | Yes | Yes | ~117 lbs | |
| *Coal/ Ton | 100-121°C | 75-90 | Yes | Yes | ~163 lbs. | |
| Electric Steam Generator/ KWh MightySteam® Products | 100°C – 1300°C Steam pressure and temperature are independently set. Variable flow rate settings. | 96 – 99 | No | No | 0 lbs. (zero) | Clean Steam |
Brief History (Chronology) of Disruptive Steam Production Methods
Instant high-temperature, variable steam, and variable backpressure.
Compare steam production methods.
Save energy and water.
On-demand rapid high-temperature steam generation.
Compare Traditional Steam Boilers to Modern Steam Generators
Steam generators are versatile. They are open-flow systems where the steam rate and back pressure can be preset. The working of the steam generator does not require pressure as an independent variable. When a pressure rating for the steam generator is specified, the rating indicates the pressure tolerance of the system. There is a lot of flexibility for applications. A pressure setting (value) can be input (user input) before the start of a cycle. This pressure setting may be the on-off trigger to turn off the generator for maximum process pressure. Or it can be an RH trigger from downstream. The unit can be preset to automatically start again quickly and make high-temperature steam if the pressure or RH value falls.
Click for Steam Generator Models.

Smart Controls for Steam Generators
Model | Temperature Range| | Back Pressure Rating| | Efficiency(nominal best to use only as an approximate guideline) | Applications(click for learning types of steam, steam industry nomenclature and applications)
|
MightySteam®OAB®(0r scroll below) | Up to 1200°C | Atmospheric- 40 bar | High 95%+ | Sterilization, chemical processing, food industry, CPG packaging.Pharmaceutical, textiles, HVAC, Testbeds. |
HGA-S | 300-1200°C | Atmospheric | 95%+ | Research and development, material testing, food testing chambers |
HGA-M | 300-800°C | Atmospheric | 95%+ | Medical sterilization, laboratory applications, mobile applications, |
Fixed or Variable Steam Flow. Instant on-off. From 4Kg/hr to Higher.
Vittori™ High-Temperature Steam Delivery Tubes
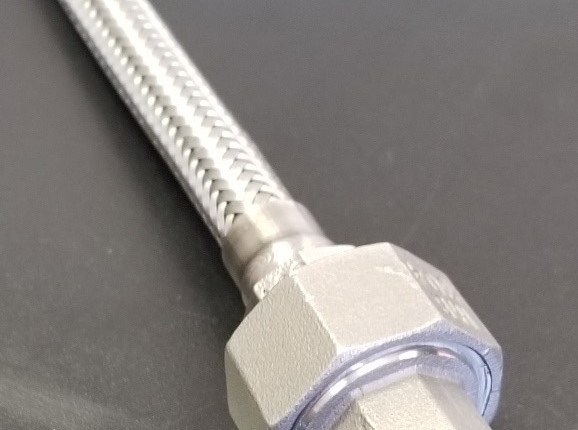

Flexible Pipe for Steam Delivery (Vittori™ Tubes)
Steam output: 1-180 kg/hr. OAB® Models
Models 4kg/hr, 12kg/hr Single Phase. Instant Steam Generation.
Models 40 Kg/hr, 100 Kg/hr and 180 Kg/hr. Three Phase models for the higher steam rate.
Three-phase systems include PLC and HMI interfaces.
Temperature Range: 250-800°C for OAB-4 and OAB-12.
Temperature range 150-800°C for OAB-40 and OAB-100
Steam Rate Flow Adjustment: Discrete and continuous modes for steam flow adjustments.
Up to 10 Bar low-price production models with backpressure tolerant models are available for high flows.
Variable Steam Flow Rate, Variable Pressure, and Variable Temperature in One Unit
Steam output: 6-12 Kg/hr Variable Steam Flow Rate.
Temperature Range: 100°C – 800°C and higher.
Steam Rate Flow Adjustment: Discrete and continuous modes. Touch screen easy change of flow.
Back Pressure Tolerant Models Available. Amazing!
Steam Superheaters for existing boilers
Air-Steam Mixtures. High humidity generators.
Air-Steam Mixture High Temperature Models HGA-M
High Specific Humidity Devices Several New Models
Hybrid Steam Air: Choose Temperature, Pressure, Air Flow and Amount of Steam
For Low Flow Rates
Steam Output: 1 kg/hr.
HGA-S Models: for Pure Steam
Temperature Maximum:
300°C (HGA-S-01) to
1300°C (HGA-CX1300)
Steam Rate Flow Adjustment: Discrete and continuous mode is available
Modern Steam Applications Technologies
Steam Chambers (Non-moving Products) – typically for R&D Tests
Steam Tunnels (Continuous Product) for Packaging and Textiles
Be compliant with modern energy and environmental demands.
Use steam above the inversion temperature.
On and Off at will.
Enjoy independent control of temperature, steam amount, and pressure.
What is saturated steam? When water molecules exist in a gaseous state at a temperature above the boiling temperature of the water, it is called the superheated steam state. The boiling temperature depends on the pressure (e.g., 100°C for 1 atmosphere, 134°C for 3 atmospheres, and so on). Steam only at the boiling temperature is called saturated steam.
What is the difference between saturated steam and superheated steam? Saturated steam is always steam at the boiling point, whereas superheated steam is at a higher temperature than the boiling point (at that pressure). The main difference between saturated and superheated steam is that saturated steam is at a two-phase (liquid and gas) equilibrium temperature. So it could contain water droplets, whereas the higher-temperature superheated steam is a high enthalpy gas (called high-quality steam as there are no water droplets). Superheated steam has a higher work potential compared to saturated steam. Work potential enables mechanical work and chemical reactions. On the other hand, Saturated steam is often classified as low-quality steam.
What is high-temperature superheated steam? Steam above the boiling point at any pressure is broadly classified as high-temperature superheated steam*. The temperature should be at least a few degrees centigrade above the boiling point to be classified as superheated steam. However, for many modern steam applications, the steam temperature has to be much higher than the boiling temperature (well into the superheated steam temperature range).
How is highly superheated steam made? Hot steam is made with rapid steam generators like the OAB® and HGA. Unlike traditional boiler technology for a high steam temperature, current steam generators avoid high pressures. The temperature for most combinatoric-steam applications should be higher than the inversion temperature (typically above 200°C) for reaping the benefits of superheated-steam-enhanced processes like drying, bio-energy production, high-level microbial and viral cleaning, energy production, antimicrobial, bio-digestion, chemical reactions, fuel production, syn-gas, methane reduction, and many others. A new area of research is the combinatory steam area for energy reduction. * MHI definition is invoked. The temperature of good superheated steam is above any inversion temperature and much higher than the equilibrium saturation temperature. The equilibrium saturation temperature is the temperature (at a given pressure) where water or water droplets can coexist with steam-gas, i.e., the boiling point. Saturation temperatures depend on pressure, e.g., ~100°C at 1 Bar or 121°C at 2 Bar, etc. Instant high quality-clean steam with high temperatures ranging from 300°C to 1300°C is now readily available for steam applications. Such applications are multiplying. OAB® and 4DSintering® are registered MHI Trademarks.
In contrast to conventional pressure boilers, steam generators produce steam quickly on start-up, produce high-quality steam, and have fewer restrictions for piping. Where is high-temperature steam typically used? Fuel Production, Antimicrobial Use, Comfort Humidity Addition, Oxidation and Erosion Studies, Food Industry, Packaging, Chemicals, Cleaning, and Materials. Bio-processes, Energy, Hydrolysis, Process Heating, Flavors, Drying, Textiles, and even the Simulation of Martian Atmospheres (Nature, December 2017). Several more applications are listed here.
What is the inversion temperature of steam? The inversion temperature is most commonly known as the temperature at which the evaporation rates into pure superheated steam and completely dry air are equal. Typically ~200°C with some dependence on the surface. The inversion temperature is the temperature for rapid antimicrobial action and rapid ceramics drying.
Multipliers to process efficiencies. High-grade, high-quality superheated steam offers a good multiplier to process efficiencies – i.e., it is SmartSteam™. Several US and International Patents protect MHI steam generators. The temperature of the MHI steam models reflects the actual steam temperature. The savings efficiencies reported are from an On to Off condition (in contrast, please note that several boiler efficiencies are reported only at a steady state)—no requirement to heat any tubes or nozzles to produce steam.
Resources: Steam Energy Calculator. Videos and Media Gallery.
Sustainability: Superheated steam enhances sustainability by reducing climate risk, accelerating energy transitions, increasing food security, and advancing health outcomes.
What superheated steam is not? It is not mist nor fog. Mist and fog have water droplets in the gas, thus the name fog. View the comparison pictures of the difference between mist/fog-steam and a high-temperature steam gas, even when produced such that the nozzle area has no mist. In the picture, please note that MHI steam generators produce mist-free gas.
Why are these devices only possible from MHI? MHI uses patented nano-structured surfaces and other novel materials that have only recently become commercially available for active steam use. MHI engineers have combined decades of thermal know-how and recent patented technologies with well-accepted/reliable MHI control systems for high-power and high-temperature steam delivery. It is a part of MHI’s overall development strategy for intelligent power in modern thermal applications. Substantial energy savings result from OAB® steam use compared to combustion heating of boilers.
Please Request Catalogs and Information.
For many facilities, steam is critical to keep processes and procedures operating within normal parameters and expectations. With this in mind, choosing a steam generation system that offers high reliability and exceptional safety while reducing energy costs and maximizing operational efficiency is essential.
|
|
Easy Fit to Industrial Production Machines and Tunnels

Large Decarbonized Steam Generators
Superheated steam uses are in – Energy, Cleaning, Heat exchangers, Textile Processing, Pulp and Paper, Cooking, Drying, Disinfection and Sterilization, Cleaning and Recycling, Drying Paint, Drying Machine Parts, and Re-forming Surfaces. Food and storage products, Tobacco Products, Textile Mill Products, Apparel, and Other Textile Products, Lumber and Wood Products, Bio mass-energy, BioPharma, Oxidation studies (inorganic and organic), Paper and Allied Products, Steam spray in hospital use, greenhouse, Soil, Printing and Publishing, Chemicals and Allied Products, Petroleum and Coal Products, Petroleum Refining, Rubber and polymers, steam injection, emulsification, Plastics Products, Steam Chest Molding, Leather and Leather Products, Stone, Clay and Glass Products, Cement, Grain, Canola, Alfa-alfa. How to specify an OAB tunnel. Antimicrobial use industries are Chemical, Hospitals, Paper/Corrugating, Power Generation, Tobacco, General Manufacturing, Animal Feed, Dairy, Hotels, Petroleum Production., Rubber, Wire and Cable, Oil & Gas, Automotive, Food Processing, Marine & Offshore, Pharmaceutical, Steel, Mining, Beverage and similar. Laboratory scale steam generation, Sterilization, Fuel cell development, Fuel processor development, Chamber and tube furnaces. Bench scale to full industrial scale.
Industries where continuous steam is used: Hydraulic, Primary Metal Industries, Blast Furnace and Basic Steel Products, Fabricated Metal Products, Industrial Machinery and Equipment, Electronic and Other Electric Equipment, Transportation Equipment, Instruments and Related Products, Chemicals/Petrochemicals, Electronics, Oil and Gas, Ethanol, pre-treatment of biomass, Pyrolysis, Oil, herbs, Steam Reforming, Complex Methane Ammonia Producing Reactions, Hydrogen reforming, Biodiesel fuels, Finishing, Food, Packaging, Printing, Paper, Pulp, Converting, Forest Products, Comfort Steam, Pharmaceuticals, Plastics, Rubber, Batteries, Electrode drying, Vinyl, Bio-solids, Sanitation, Disinfection, WGSR reactions, Low oxygen content H2O gas, so dry and could sometimes even be for sterilization, Soil re mediation, steam stripping of Volatile, industrial propane dehydrogenation processes, Pulp, hog/animal-fuel, clean or emulsify bark sludges, Reverse water gas-shift reactions and flavor reactions, Lumber and/or efficient Paper-drying, peat/jute drying, Gasification-reactor, Consider for vacuum production steam in ejector nozzles with steam or steam air mixes with over 50m/s steam exit velocity, Textile-drying, Drying. Swelling Starch, Starch Granules, Starch Gelatinization. Cleaning with MightySteam • Humidification for Dry and Humid Atmospheres in Ceramic and Paper Rolls and Comfort Processing, Work, and Propulsion by Steam, Heating, Sterilization, Vacuum, and oven use. Atomization of Fluids, Motorization, and Modification. Waste to Fuel Prototype and Simulation. Ask MHI for Sample Catalytic Surfaces Quasi R or ceramic substrates that can take catalysts.
Steam Chambers up to 1300C for oxidation and food contact studies in a pure steam environment.
Steam for Packaging and Textiles
While several applications offer down-the-line energy efficiencies with high-temperature superheated steam use, one typical application is to make hydrogen with steam reforming of methane or organic materials; here, the higher temperatures give rise to considerably better reaction efficiencies. Food Safety Use. Food Security. Vertical Farming. Dryer Configurations: Batch/Cabinet, Can/Drum, Continuous/Conveyor, Deck, Loop, Loft, Paddle, Ring, Roll/Cylinder, Rotary, Shelf/Tray/Truck, Skin (both artificial and inorganic), Tensionless, Frame, Tower, Tunnel, Warp, Web, Wicket. Dryer Types Possible: Centrifugal, Combination Infrared/Convection, Attenuate CFC and HCFC Conduction, Convection – Counterflow, Convection – Impingement, Convection -Flotation, Convection, -Through-Air, Dehumidifying, Flash, Fluid-Bed, Infrared – catalytic, Infrared – Longwave, Infrared – Medium-wave, Infrared – Short -wave, Microwave, Radio Frequency, Spray, Steam, Vacuum. Energy Source: Dual Fuel, Electricity, Steam. Materials Dried, Food, Paste/Mixes, Powders, Slurries, Solids, Solvent- and Water-based Materials. Manufacturing Process: Calcining, Curing, Dehydrating, Drying, Dry sand, and investment molds, Finishing, Fusing, Granulating, Heat Setting, Acoustics, Research, Heat Shrinking, Laminating, Moisture Profiling, Pasteurizing, Pre-and Post-Drying. Industries Served: Chemicals/Petrochemicals, Electronics, Alternatives to Waste Heat Boilers Augmented, Oil and Gas, biotic and abiotic cleaning, Ethanol, Biodiesel Fuels, Hydrolysis, Finishing, Food, Packaging, Printing, Paper, Pulp, Converting, Forest Products, Pharmaceuticals, Plastics, Rubber, functionalize graphite, graphene, Boron nitride, Vinyl. Biosolids include Sterilization, Soil remediation-steam stripping of volatile, Pulp, hog-fuel, bark sludges, Paper Drying, Peat/Jute Drying gasification reactor, Textile drying, salt drying, and reclamation. If you use steam, steam, water, and steam air mixes in de-Superheaters, better control could be achieved with OAB® or HGA-M models. Steam Tunnels.
MHI systems are used for fuel production in Gasification, Pyrolysis, Combustion, Digestion, or even Fermentation, enhancing kinetics.
Have you considered Flash removal with Steam or Cascade e-ion (de-Flashing)?
Volumetric Specific Heat of Steam at 30 Bar = 51 kJ/m3.K
Volumetric Specific Heat of Steam at 2 Bar = 2.4 kJ/m3.K
Volumetric Specific Heat of Iron = 3537 kJ/m3.K
Volumetric Specific Heat of Water (25C-100C) = 4137-3770 kJ/m3.K